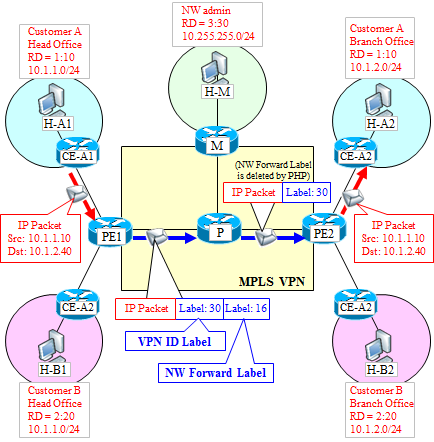
The router of the description in the basic configuration and the view of the MPLS-VPN is shown below.
The details of the VRF is an MPLS-VPN of critical components, please see this page .
CE-A1, CE-A2, CE-B1, CE-B2
A router called the Customer-Edge-Router, the customer side of the router at the boundary of the customer's corporate network and MPLS-VPN network. Normal will be the rental routers from provider or the customer's assets.
PE1, PE2
A router called the Provider-Edge-Router, the provider side of the router at the boundary of the customer's corporate network and MPLS-VPN network. In the PE virtual router called VRF is made each customer, and manages the routing individually.
M
Maintenance-Router (M router). It is not a common name, but it has been arranged for description of an example of the Route-Target. Here we assume that there is a segment to perform the maintenance and operation of the entire MPLS network.
P
A router called Provider-Router (P routers). Relay routers in the MPLS network. Usually it is to ensure a redundant path between each PE and M is two or more, but here we are to each router 1 route for clarity of illustration.
The flow of communication
First, when a packet enters from the CE-A1 to VRF instance for PE1 customer A, (in the Figure 30) VPN ID(identification) Label (Inner Label) is attached. The VPN ID Label is intended to receive along with the VPNv4 Prefix in BGP from PE2, to identify which VRF instance you go to in PE2 side. (When exchanging the route information by MP-BGP, judgement of which VRF the packet may go to is done by Route Target, but when forwarding packet by MPLS, it is done by VPN ID Label. )
The VPNv4 Prefix is the combination of Route Distinguisher (RD) and the usual prefix [RD: Prefix]. In the case of the figure, and represents a network that is connected to the CE-A2 in VPNv4 Prefix, [1:10:10.1.2.0/24] .
RD (Route Distinguisher) is an identifier to avoid duplication of the customer's IP address information in the network, will be used to identify whether something that Prefix is of any customer. (Unlike Route-Target, there is no ability which VRF to go. You are simply used for the purpose to avoid duplication of the IP address on the BGP.)
At the same time VPN ID Label is attached at the PE1 of the VRF instance, the packet will be moved to the Global instance from the VRF instance.
The Global instance, since the NextHop is a 2.2.2.2, a NW Forwarding Label (Outer Label) corresponding to (16 in the figure), and further mounted on the VPN ID Label attached earlier (the stack). The NW Forwarding Label is what is transmitted from P by the LDP and the like.
When the P router receives an MPLS packet, and switching in the network to look at only the NW Forwarding Label in MPLS network. P router is only one in this example, but even if there are any number of P router in between, in all of P router will continue to switching to look at only NW Forwarding Label.
The P router which is placed to the previous PE2 remove the NW Forwarding Label by PHP and transfer the packet to PE2.
The PE2 recognize a packet attached the label sent in BGP by itself, and at the same timing of popping the VPN ID Label, the packet is transported from the Global instance to the VRF instance that corresponds to the VPN ID Label, where to forward the IP packet to the CE-A2 by normal routing you.
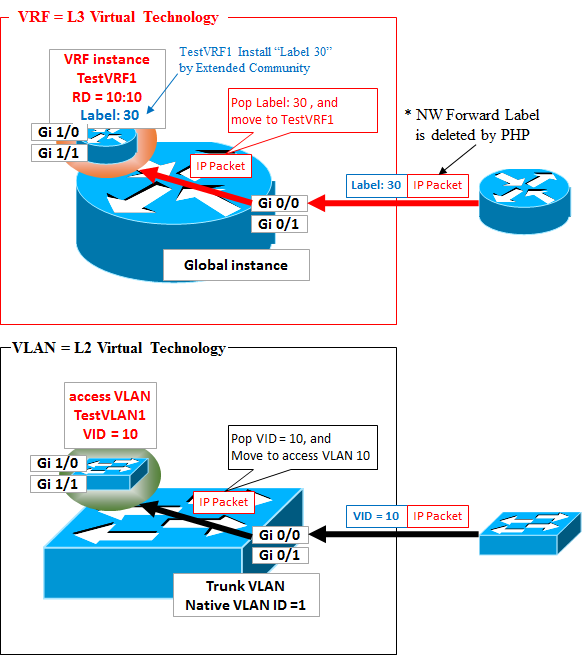
This behavior of popping label and instance transport is similar to the one of popping VLAN tag and access VLAN transport in the switch.



コメント