IP address is the address on network communication.
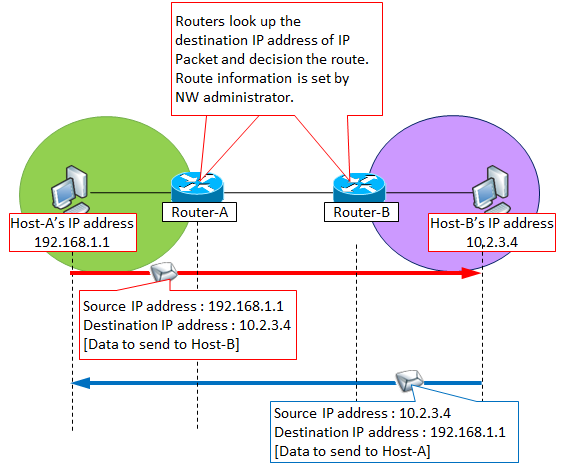
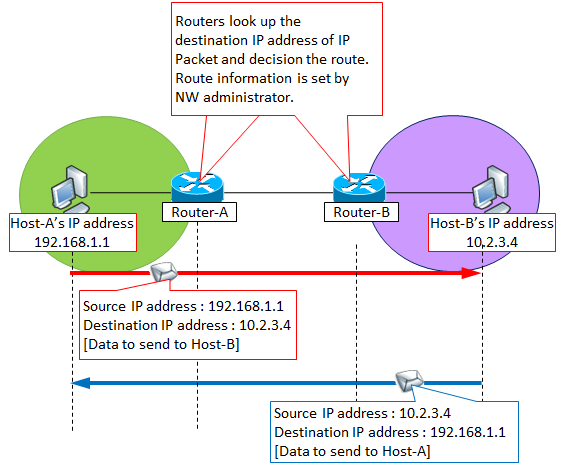
For example, when Host-A wishes to communicate with Host-B, Host-A adds the information "Source IP address = Host-A's IP address" + "Destination IP address = Host-B's IP address" in the communication data.
The NW device such as a "Router" looks up the IP address of Host-B as the destination, decides the communication route, and eventually arrives at Host-B. These route decision processes are called routing.
If Host-B wishes to reply to Host-A, it also communicates in the same way with the information "Source IP address = Host-B's IP address" + "Destination IP address = Host-A's IP address".
Nowadays, IP is the world standard communication method used on the Internet. IP addresses are always allocated to terminals and network devices that communicate with the Internet.
The IP address is composed of 32 bits, converted to decimal number by 8 bits, and it is expressed as being separated by dot(.) .
Below is an example of communication between Host-A having an IP address of 192.168.1.1 and Host-B having an IP address of 10.2.3.4.
Usage according to IP address range
The IP address range is from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255, but the usage is determined by the range. Specifically, it is below.
| IP address range | Assign | Usage |
| 0.0.0.0~0.255.255.255 | Reserved | Display of default route and so on. |
| 1.0.0.0~126.255.255.255 | Class A | For Generic Unicast Packet |
| 127.0.0.0~127.255.255.255 | Loopback | Used when a host communicate with itself (i.e. Used when specifying itself as a DNS server) |
| 128.0.0.0~191.254.255.255 | Class B | For Generic Unicast Packet |
| 191.255.0.0~191.255.255.255 | Reserved | Not assigned |
| 192.0.0.0~223.255.254.255 | Class C | For Generic Unicast Packet |
| 223.255.255.0~223.255.255.255 | Reserved | Not assigned |
| 224.0.0.0~239.255.255.255 | Class D | For Generic Multicast Packet |
| 240.0.0.0~255.255.255.255 | Class E | Reserved (Experimental, Broadcast address and so on.) |
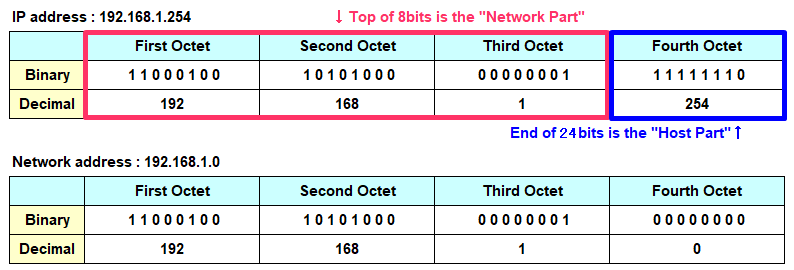
Network Address
IP address can be divided into a "Network Part" and a "Host Part", and an address expressing a "Network Part" is particularly called a "Network address". For example, if there is an address of 192.168.1.254, and the Network Part is 24 bits from the top, the Network address is 192.168.1.0. Note that this network address can not be set as an IP address on the terminals or NW devices.
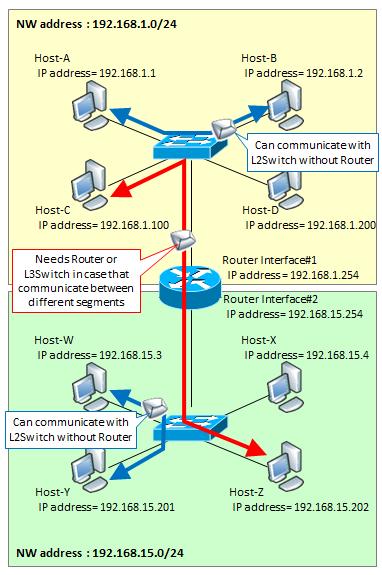
Network addresses may also be referred to as "Network Segments", or simply "Segments", by alias.
Hosts in the same Network Segment can communicate with each other only by a hub or an L2 switch, and hosts in different Network Segments can communicate with each other through routers or L3 switches. Please refer to here for details.
In the example above, we assume that the "Network Part" is "24 bits" from the beginning, but there are two ways to decide how many bits to set. One is based on the idea of classful and the other is based on the idea of subnet mask.
Classful
Classful means that the number of bits in the "Network Part" is determined by the range of the IP address. Specifically, it is as follows.
Class A's range = 1.0.0.0 - 126.255.255.255
In case of Class A, 8 bits from the beginning is the Network Part. For example, if the IP address is 10.2.3.4, the network address will be 10.0.0.0.
Class B's range = 128.0.0.0 - 191.254.255.255
In case of Class B, 16 bits from the beginning is the Network Part. For example, if the IP address is 172.20.30.40, the network address will be 172.20.0.0.
Class C's range = 192.0.0.0 - 223.255.254.255
In case of Class C, 24 bits from the beginning is the Network Part. For example, if the IP address is 192.168.33.44, the network address will be 192.168.33.0.
Subnet Mask (Classless)
The idea of classful is almost not used now. The reason is that efficient allocation is impossible due to depletion of IP address. Particularly in class A, the theoretically host unit can allocate terminals of 2 to the power of 24 ≈ 16 million, but in reality such a configuration is impossible.
It is better to put about 256 terminals at various network addresses than that. Therefore, we removed the concept of class so that we can freely decide the network part with all IP addresses. That is the Subnet Mask. Also, this idea is called classless.
For example, if there is a notation "1.1.1.1/28", "1.1.1.1" means IP address and "/28" indicates Subnet Mask which saids "the first 28 bits are Network Part".
In addition, like "192.168.0.0/16", the Network Part which was 24 bits in the classful is reduced to 16 bits, "/16" is also called a Supernet Mask, but in many case, call it Subnet Mask.
This classless routing support is called CIDR (Classless InterDomain Routing), and the method that Routing Protocols that did not originally support CIDR (RIPv 1 etc) supports CIDR with limitasions is called FLSM (Fixed Length Subnet Mask) . And, the method which is created for overcoming the FLSM limitasions is VLSM which is handled by RIPv2, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, and so on. Many commentaries are difficult to understand in this topics, but this article details the intelligible explanation in detail.
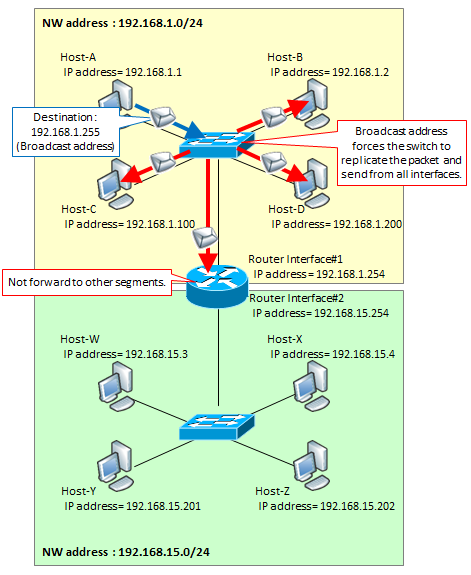
Broadcast address
It was explained that the first IP address of the Network Part is called a Network address, but on the contrary, the last IP address of the Network Part is called a Broadcast address.
Packets destined for this broadcast address are duplicated and transmitted from all ports when received by the switch. That is, it broadcasts to all terminals and routers in the same segment. Like the Network address, this broadcast address can not be set as an IP address on the terminal or NW devices.
Private IP address
A host that communicates in the IP network must have a unique IP address assigned to the NW network. In the IP network that connects the world as the Internet, there are not enough IP addresses to assign unique IP addresses to all the devices recently. Therefore, it is common to use a private IP address to be used in units such as company. And, because private IP address can not connect to the Internet (can not return), it is common to use PAT only when it comes to the Internet.
The private IP address is used in an IP network such as a company and can be the same (non-unique) address as other companies. The private IP address is the following address band.
172.16.0.0~172.31.255.255 = 172.16.0.0/12
192.168.0.0~192.168.255.255 = 192.168.0.0/16
And, in order to realize communication between private IP addresses over the Internet, a technology called Internet VPN is required. As mentioned above, Private IP addresses can not uniquely define routes on the Internet and can not be routed.
Special address range
192.0.2.0/24
This address band is reserved in the global address band which can be used for explanation of configuration guide etc. of each maker. (It is supposed not to be used in actual communication)
169.254.0.0/16
This address band is an IP address band automatically generated when IP automatic acquisition is done and IP can not be acquired from DHCP. Generally, the lower 16 bits are generated uniquely from the MAC address. Also, it seems that this address band is being diverted also for connection with Amazon AWS recently.
How to check your IP address
If it is Windows, you can check it by typing "ipconfig" from the command prompt.
- Windows Key + R
- Type "cmd" in the [Run] input BOX, and press Enter
- At the popped up command prompt, type "ipconfig" and press Enter
The number next to [IPv4 address . . . . . . . . . . . .: ] is IP address.
In this column, if private IP address is displayed instead of global IP address and communication is possible with the Internet, it is NAT (PAT) converted by the router. For NAT, please see here.
If you want to check the IP address after NAT conversion, you can check it on the site etc. below.
Next to the message "Your global IP address is:" is the IP address after NAT conversion.



コメント