MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) is the switching method which adds a label to various L2 / L3 protocol (such as IPv4 / IPv6 / Ethernet / ATM / Frame-Relay), and transfer the protocol at high speed based on the label .
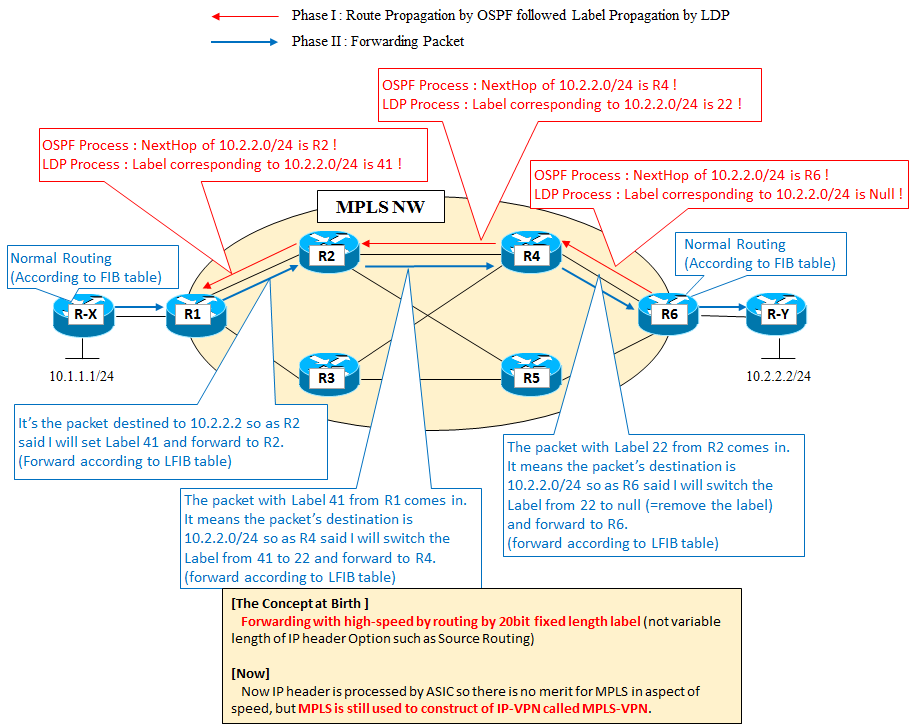
A specific flow by MPLS is shown below.
First propagates the route information by routing protocols such as OSPF.
Then propagates the label information corresponding to the route information by the label propagation protocols such as LDP. Label is a number from 0 to about million. As in the example below, there is no problem even if the label number corresponding to the route information is shared for other routers which associate MPLS network. When the Label propagation has done, it will be ready to be the data transfer.
And when the packet with MPLS label comes in, the router forwards the data to destination indicated by label with switching the label.
In the IP packet routing, IP header length is variable( 32bit destination IP address is mainly checked but in the special case, the options such as source routing also must check) but in MPLS network, only 20bit label (fixed length) is used to be judged, it is possible to forward the packets with high-speed.
However, this is the story of the era that the routing had done by software processing (CPU processing), this advantage does not have most recently, because the recent routers' routing is also hardware processing (ASIC processing).
MPLS is has been originally developed as a high-speed transfer technology of the time to carry IP over ATM, you as the current utilization method is VPN construction of MPLS-VPN has a big weight.
MPLS has two modes. one is called framd mode(packet mode) which header of 20bit including the label between the data link header and an IP header (Shim header), and another is called cell mode which maps ATM VPI / VCI or Frame-Relay DLCI to the label. But recently Ethernet has become the mainstream of the layer2 network, here's take a look at the frame mode to the main.
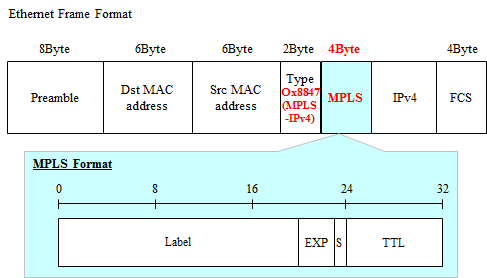
The format of the MPLS header (Shim header)
The format of the MPLS header for attaching the MPLS label to the IPv4 over Ethernet (Shim header) is shown below.
Label Field
20bit. Identifier to determine the destination. It should be noted, Label is assigned to each FEC (Forwarding Equivalence Class) instead of the destination NW address.
The FEC is, in brief, "in MPLS NW, collection of packet desired to be the same behavior". In the case of unicast, e.g., the destination NW address or ToS value, or a combination thereof, etc, it will be classified. However, it will be in most cases "FEC = destination NW address". For multicast, for example, it is classified by such a combination of source / destination IP address.
EXP Field
3bit. At the bit to be experimental use, it has now been utilized in mapping the information of the IP Precedence for the purpose of QoS.
S Field
1bit. Stack bit. MPLS header is possible to be put two or more in one packet. If this stack bit is 0, it indicates further that the MPLS header is followed by the MPLS header. If the stack bit is 1, that after the MPLS header is followed by the protocol for transferring such IPv4.
In MPLS-VPN, you have to use two of the MPLS header in one packet.
TTL Field
8bit. As TTL of the IP header, it will be used for loop prevention. It can also be newly set at the timing when MPLS label is mounted, and can also be set the TTL value in the IP header as it is (it is called TTL Propagation).

コメント
Thanks for sharing your thoughts. I truly appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for
your next post thank you once again.
We stumbled over here from a different web address and thought I
may as well check things out. I like what I see so i am just following
you. Look forward to looking into your web page repeatedly.