In the memory of the NW devices of Layer 3 (router or L3 switch), there is a space to store the routing information called routing table. The router or L3 switch forward the incoming packet to the appropriate path matched for the table information. Routing tables are generally described per Network Address, rather than IP Address.
Configuring the routing, the information is stored in the routing table.NW address to which IP address assigned to interface of device belongs is pre-installed to the routing table as "Connected", which means directly connected network address on the device.
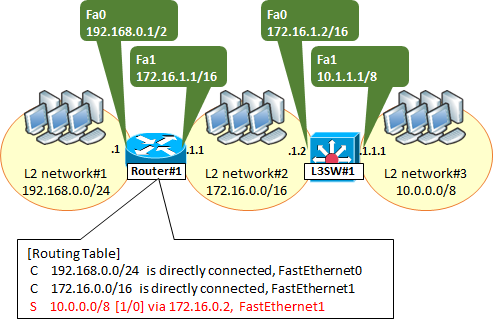
Since routing table's view is different by the vendor, we will look at the view as an example of Cisco.The following shows an example of the routing table with one static route.
Examples of a Routing Table
C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0
"C" means "Connected" network, that is directly connected to the network.
192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected to the FastEthernet0 (Fa0) interface, it means that.
C 172.16.0.0/16 is directly connected, FastEthernet1
Like the above, 172.16.0.0/16 is connected directly to the Fa1, it means that.
S 10.0.0.0/8 [1/0] via 172.16.1.2 , FastEthernet1
"S" means a Static Route.
For Dynamic Routing, RIP if "R", OSPF if "O", is EIGRP if "D" is displayed.
In the notation of [1/0], 1 Administrative Distance, 0 means the Metric (Cost).
Administrative Distance is the value indicating the routing of trustness. If it is transmitted from a completely the same route information from different Dynamic Routing Protocol, it trusts the information that this value is smaller, and puts the route in the routing table. The default value is determined as follows.(Other than Connected is also possible to change the settings)
| Protocol | Administrative Distance |
| Connected | 0 |
| Static | 1 |
| EIGRP summary route | 5 |
| BGP (EBGP) | 20 |
| Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol | 90 |
| IGRP | 100 |
| OSPF | 110 |
| IS-IS | 115 |
| RIP | 120 |
| ODR | 160 |
| EIGRP (External: re-delivery) | 170 |
| BGP (iBGP) | 200 |
Metric is different by routing protocol's definition, but omitted here in the description. Will be zero even if any case of Static route.
"via 172.16.1.2" means that NextHop is 172.16.1.2, the next "FastEthernet1" means the transmission interface.The NextHop, is the IP address of the next destination.
About Point-to-Point interfade, such as Serial interface, PPPoE interface, virtual interface of the GRE, NextHop is fixed if sending interface is determined. But about multi-access interface, such as Ethernet, NextHop Candidates are several even if sending interface is determined.So, NextHop in a multi-access interface should be determined not only sending interface but IP address, and it ensures that destination is unique.
The study of the network foundation, the following books are recommended.

コメント